Content last revised on January 22, 2026
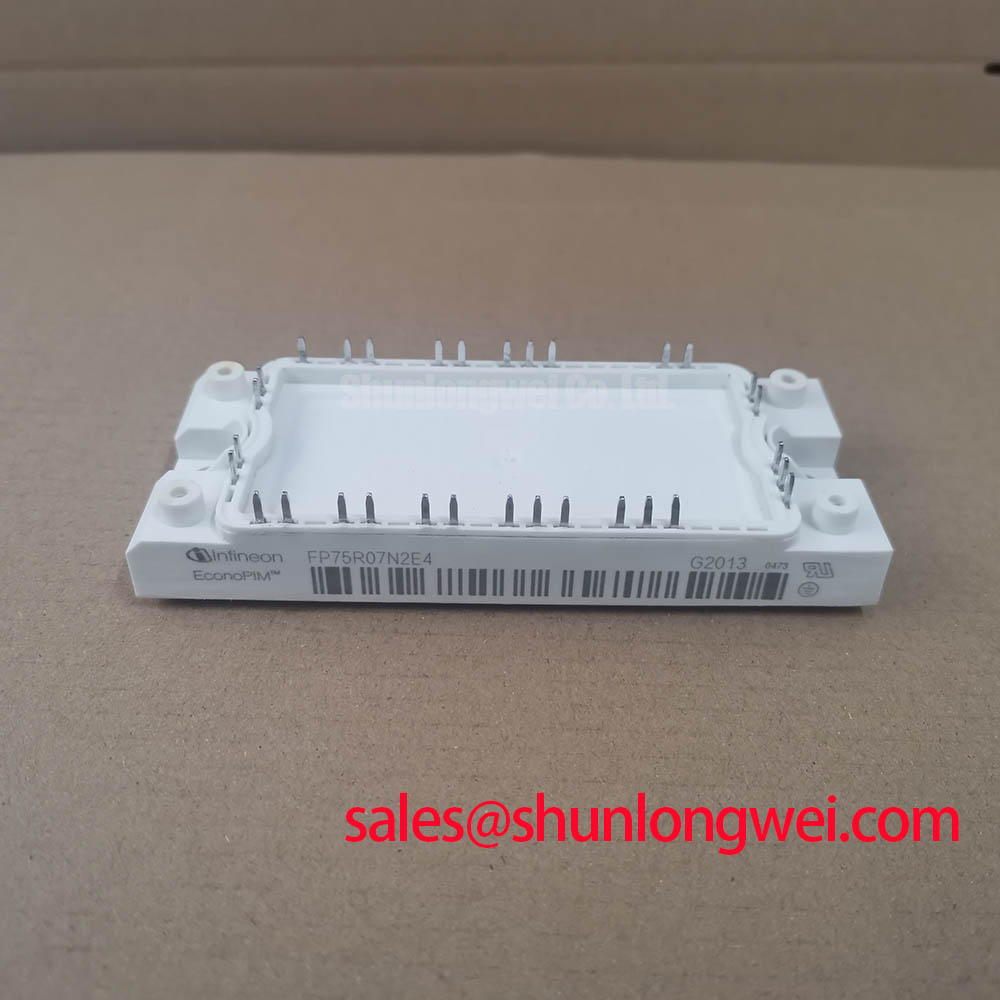
FP75R07N2E4: 650V PIM IGBT Module for Compact Motor Drives
Streamlining Power Stage Design for Enhanced System Reliability
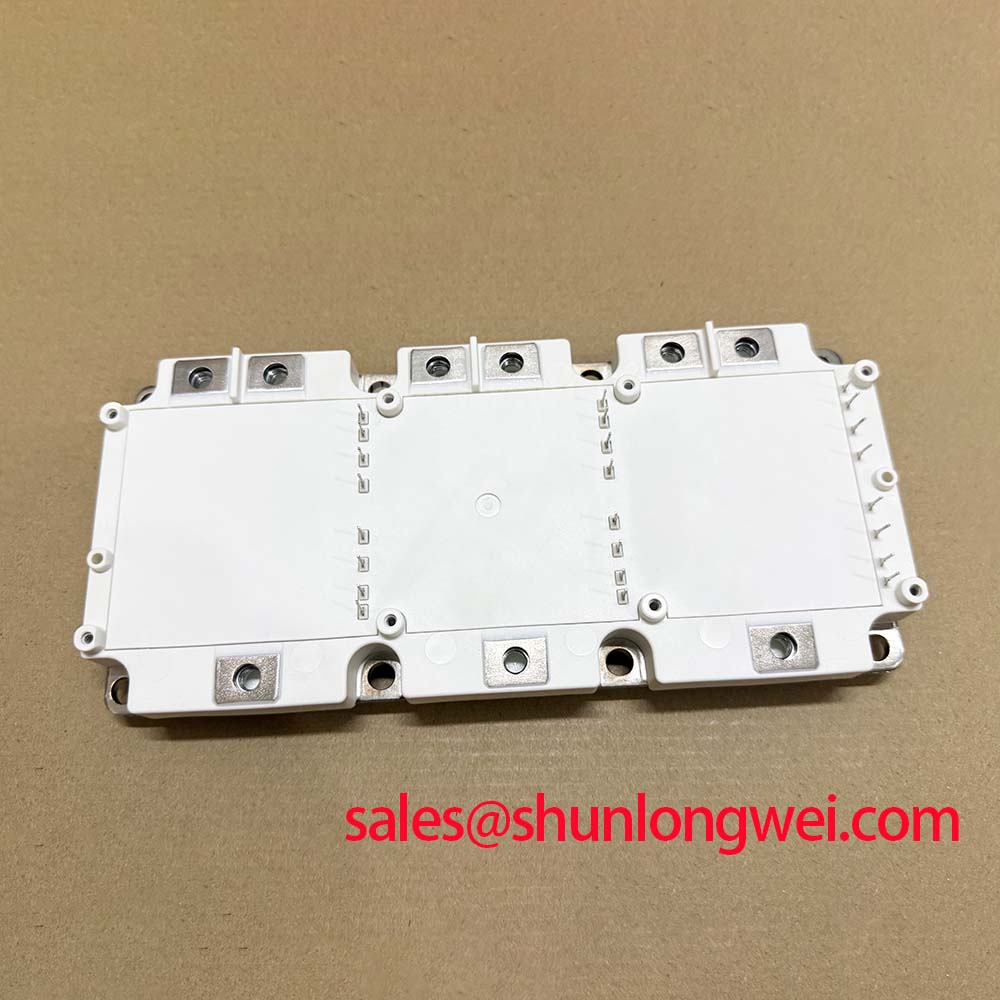
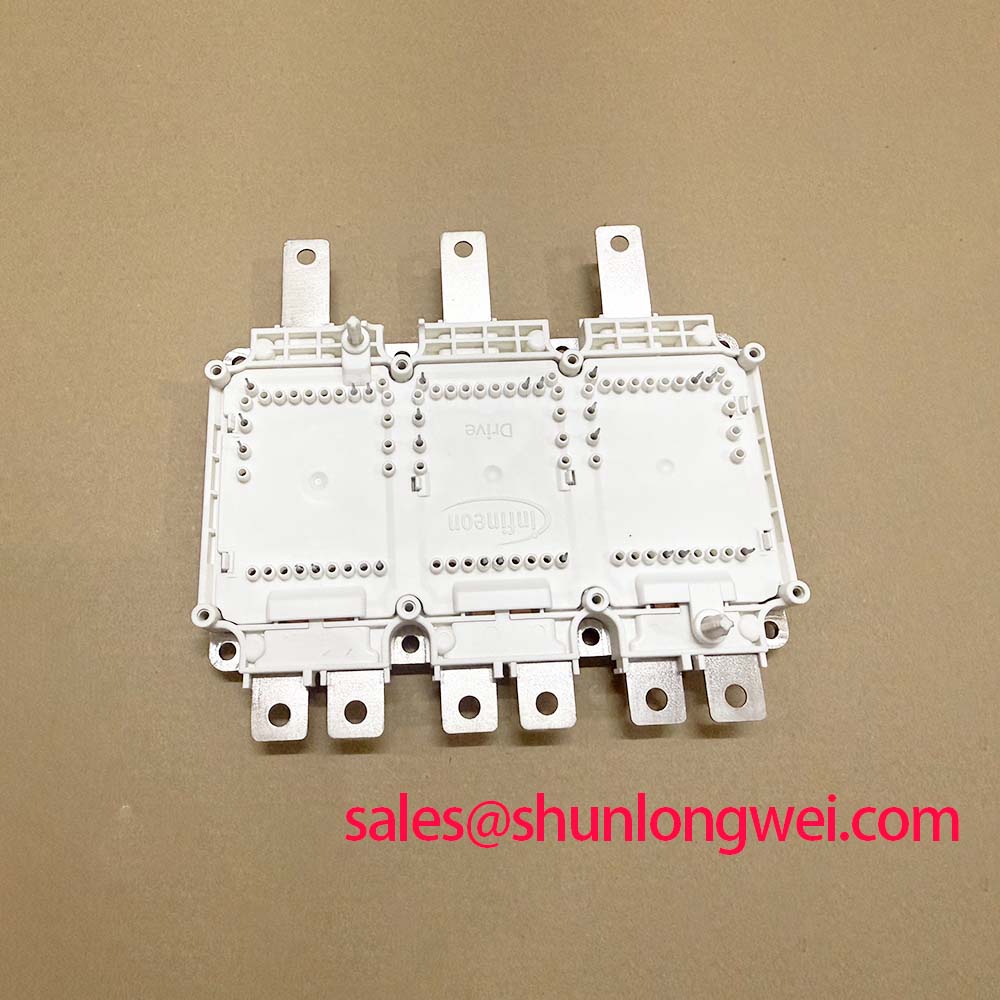
The Infineon FP75R07N2E4 is a 650V, 75A Power Integrated Module (PIM) engineered to simplify the design and assembly of variable frequency drives while enhancing thermal management. With a specification of 650V | 75A | Three-Phase Inverter, this module combines a three-phase input rectifier, brake chopper, and a three-phase inverter into a single EconoPIM™ 2 housing. Key benefits include accelerated assembly via PressFIT pins and precise thermal oversight with an integrated NTC sensor. This integrated approach directly addresses the engineering need for reducing board complexity and component count, which is critical in achieving higher power density in modern compact drive systems.
Application Scenarios & Value
Optimizing Assembly in High-Volume Drive Manufacturing
The FP75R07N2E4 is tailored for applications where both performance and manufacturing efficiency are paramount. Its architecture is particularly beneficial in servo drives, general-purpose motor drives, and auxiliary inverters where space is constrained and reliability is essential. The integration of the input rectifier, brake chopper, and inverter stage into one compact module substantially reduces the required PCB real estate compared to discrete or multi-module solutions. This consolidation simplifies the bill of materials, minimizes interconnection parasitics, and lowers the overall system assembly complexity. For applications requiring a higher voltage rating, the FP75R12KE3 offers a 1200V alternative within a similar package concept. What is the key advantage of its integrated topology? It reduces assembly steps and potential points of failure, directly enhancing system reliability. For compact motor drives up to 30 kW prioritizing simplified assembly, the FP75R07N2E4's integrated three-phase bridge and PressFIT mounting offer a definitive advantage over discrete solutions.
Intra-Series Comparison & Positioning
Balancing Voltage, Current, and Integration
Within the broader landscape of power modules, the FP75R07N2E4 occupies a specific niche defined by its 650V rating and 75A nominal current in a highly integrated PIM format. Unlike modules that only feature an inverter stage, the FP75R07N2E4 provides a near-complete power conversion front-end and motor drive solution. This makes it an excellent choice for systems operating on 200-240V AC lines, where the 650V blocking voltage provides a robust safety margin. While other modules may offer higher current or voltage, they often do so in larger packages or with less integration, requiring additional external components like rectifier bridges. This module's value proposition is centered on delivering a balanced set of specifications in a format that accelerates time-to-market by simplifying the overall power stage engineering effort.
Key Parameter Overview
Core Specifications for System Evaluation
The technical specifications of the FP75R07N2E4 are optimized for motor drive applications. The parameters below highlight its core capabilities, providing a foundation for design-in decisions. For complete details, please refer to the official datasheet.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCES) | 650 V |
| Nominal Collector Current (IC nom) | 75 A |
| Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage (VCEsat, typ. at IC nom) | 1.55 V |
| Maximum Junction Temperature (Tvj op) | 150 °C |
| Configuration | Three-Phase Input Rectifier + Brake Chopper + Three-Phase Inverter |
| Mounting Technology | PressFIT |
Technical Deep Dive
Inside the EconoPIM™ 2: A Focus on Integration
The FP75R07N2E4 leverages Infineon's Trench/Fieldstop IGBT4 technology, which provides a balance between conduction losses (VCEsat) and switching losses, making it well-suited for the typical switching frequencies found in motor drives (2-15 kHz). A key feature is the PressFIT mounting technology. This solder-free connection method simplifies the manufacturing process by creating a reliable, gas-tight cold-welded joint between the module pins and the PCB. This eliminates the thermal stress of a wave soldering process, enhancing long-term reliability. Furthermore, the integrated NTC thermistor provides a direct, real-time temperature feedback mechanism. How does an integrated NTC improve system design? It allows for precise thermal monitoring of the module, enabling proactive thermal management and fault protection without the need for an external sensor, thus simplifying the control circuitry.
Industry Insights & Strategic Advantage
Meeting the Demands of Modern Industrial Automation
In the context of Industry 4.0 and advanced automation, the demand for smaller, more efficient, and more reliable motor drives is constantly increasing. The FP75R07N2E4 directly supports these trends. By integrating multiple power stages into a single module, it enables the design of more compact drive systems, which can be located closer to the motor, reducing cabling and improving response times. The inherent reliability of the integrated design and the solder-free mounting process contribute to a lower total cost of ownership by reducing manufacturing defects and improving field serviceability. This positions the FP75R07N2E4 not just as a component, but as a strategic enabler for developing next-generation, high-density power conversion systems that are essential for modern industrial applications. For further reading on the foundational technology, explore this in-depth analysis of IGBT modules.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary benefit of using a Power Integrated Module (PIM) like the FP75R07N2E4 over discrete components?
Using a PIM like the Infineon FP75R07N2E4 significantly simplifies system design and assembly. It combines the rectifier, brake chopper, and inverter into a single, thermally optimized package. This reduces PCB space, minimizes parasitic inductance and resistance from interconnections, and streamlines manufacturing, leading to a more compact, reliable, and cost-effective final product.
2. What are the best practices for mounting a PressFIT module like the FP75R07N2E4?
Proper mounting of a PressFIT module is critical for ensuring a reliable connection. It requires a precisely tooled press-in block that applies even pressure across all pins simultaneously. The PCB hole tolerances (plated-through hole diameter) must strictly adhere to the specifications in the datasheet to create the required cold-weld connection. Unlike soldering, this is a mechanical process that must be carefully controlled for optimal results.
3. How does the integrated NTC thermistor in the FP75R07N2E4 enhance system protection?
The integrated NTC thermistor is placed close to the IGBT and diode chips, providing a more accurate and faster-responding measurement of the module's operating temperature compared to an external sensor on the heatsink. This allows the drive's control system to implement precise over-temperature protection (OTP), derating the output power or shutting down the system before catastrophic failure occurs, thus improving the overall prevention of IGBT failure.
4. Is the 650V VCES rating sufficient for 400V AC line applications?
No, the 650V VCES rating is not recommended for direct-on-line 380/400V AC systems. This rating is primarily intended for 200/240V AC line applications, where the rectified DC bus voltage is typically around 320VDC. For 400V AC systems, which can have DC bus voltages exceeding 560VDC and significant voltage spikes, a module with a 1200V rating, such as the FP75R12KT4_B11, is the appropriate engineering choice to ensure a safe operating margin.
As the power electronics landscape evolves towards greater integration and higher power densities, modules like the FP75R07N2E4 offer a forward-looking solution. By consolidating key power stages into a single, reliable component, it provides engineers with a strategic tool to develop more competitive and robust systems for a wide array of industrial applications.