In an era defined by the pursuit of high efficiency, electrification, and green energy, a pivotal technology is silently powering the world’s most critical innovations: the IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) Module. As the heart of modern power electronics, the IGBT module’s exceptional ability to handle high voltages, manage large currents, and deliver precise power control has made it indispensable across numerous key industries.
From the electric car you drive to the giant blades of a distant wind farm and the automated machinery in a smart factory, IGBT modules are the unseen heroes working behind the scenes. This article will take you on a deep dive into the seven key application areas of IGBTs, revealing how they have become the core technology driving our future.
1. Electric & Hybrid Vehicles (EVs/HEVs): The Heart of Green Mobility
In the automotive industry’s seismic shift towards electrification, the IGBT module plays the dual role of a central nervous system and a powerful heart for the vehicle’s powertrain.
- Core Function: The IGBT is the absolute cornerstone of an EV’s motor controller (inverter). It is responsible for efficiently converting the Direct Current (DC) from the battery into the Alternating Current (AC) needed to power the electric motor, precisely controlling its speed and torque.
- Key Advantages:
- Efficient Propulsion: High-performance IGBTs significantly reduce energy loss during power conversion, which directly translates to a longer driving range for the EV.
- Energy Regeneration: During braking or deceleration, the IGBT module enables regenerative braking by reversing the energy flow, converting the car’s kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery.
- Robust Reliability: Automotive-grade IGBT modules are designed for extreme durability and stability, ensuring safe and reliable vehicle operation under all driving conditions.
The performance of the IGBT directly defines an electric vehicle’s power, efficiency, and overall reliability.
2. Industrial Motor Drives (VFDs): The Conductor of Smart Manufacturing
In the world of industrial automation, the efficient operation of countless motors—from machine tools and conveyor belts to large-scale fans and pumps—relies on Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). The IGBT module is the core power-switching component within these drives.
- Core Function: Through high-frequency switching, IGBTs precisely adjust the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to an electric motor, enabling seamless and continuous speed control.
- Key Advantages:
- Energy Savings: By matching the motor’s speed to the load’s demand, VFDs prevent the energy waste associated with running motors at full speed, often achieving energy savings of 30% or more.
- Process Optimization: Precise speed and torque control elevates the level of automation and improves product quality in manufacturing processes. Industry 4.0 principles
- Reduced Losses: The low switching loss characteristic of IGBTs leads to higher overall efficiency and less heat generation in the VFD.
In the pursuit of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, IGBT-based drive technology is a fundamental pillar for achieving energy efficiency, productivity, and intelligent control.
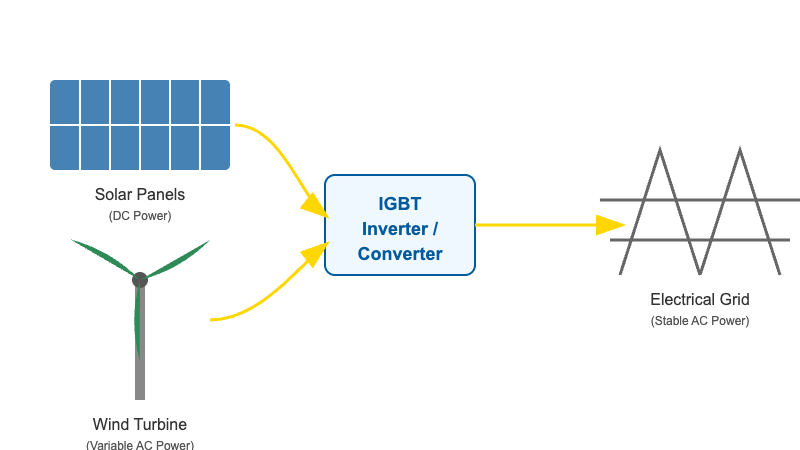
3. Renewable Energy Systems: The Gateway for Clean Power
Solar and wind power are pillars of our future energy mix, but they generate unstable DC or variable-frequency AC power. The IGBT module acts as the essential “power translator” in these systems.
- Core Function:
- Solar Inverters: IGBTs efficiently convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into grid-compliant AC electricity, enabling photovoltaic power to be fed into the public grid or used locally.
- Wind Turbine Converters: In wind power systems, IGBTs are used in converters to transform the variable-frequency AC power from the turbine into DC, and then invert it back to stable, grid-frequency AC power.
- Key Advantages:
- High Conversion Efficiency: This directly determines how much of the captured renewable energy is successfully utilized. Every percentage point of efficiency gained translates to a significant increase in generated power.
- Grid Stability: IGBTs ensure the output power is clean and stable, which is critical for maintaining the health of the electrical grid as renewable penetration increases.
Without efficient and reliable solar and wind power IGBTs, clean energy cannot be seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
4. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): The Guardian of Critical Systems
For mission-critical facilities like data centers, hospitals, and financial institutions, even a millisecond of power loss can be catastrophic. The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is their lifeline, and the IGBT is the guarantor of its reliability.
- Core Function: When utility power fails, the IGBTs within a UPS system instantly activate, converting the DC power stored in backup batteries into a pure, stable AC sine wave to provide seamless power to critical equipment.
- Key Advantages:
- Instantaneous Switching: Ensures a zero-interruption transfer to backup power, protecting sensitive electronics from data loss or damage.
- Power Conditioning: Even when mains power is active, the UPS uses IGBTs to regulate voltage and filter out power disturbances, providing high-quality power at all times.
- High Reliability: Guarantees that the UPS can perform flawlessly when it’s needed most.
5. Rail and Traction Systems: The Powerhouse Behind Heavy-Duty Transport
High-speed trains, subways, and electric locomotives are true powerhouses on rails, with extremely demanding requirements for power and reliability.
- Core Function: The IGBT module is the central component of a train’s traction converter. It manages the high-voltage power drawn from the overhead lines and converts it into the immense power required to drive the massive traction motors.
- Key Advantages:
- Extreme Power Handling: Capable of withstanding thousands of volts and thousands of amperes, providing the immense torque needed for acceleration and hauling heavy loads.
- Ultimate Reliability: A robust mechanical and electrical design allows IGBTs to thrive in the harsh railway environment, enduring constant vibration, wide temperature swings, and electrical stresses to ensure passenger safety and operational uptime.
The advancement of IGBT technology has been a key enabler for the world-leading performance of modern high-speed rail systems. High-speed rail technology overview
6. HVAC and Induction Heating: The Pacemaker of Efficiency
Beyond these large-scale applications, IGBTs play a vital role in enhancing efficiency in other important sectors.
- HVAC Systems: In large commercial Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, IGBTs are used in VFDs to control compressor and fan motors. By intelligently modulating their speed, they achieve significant energy savings and provide more stable, comfortable climate control.
- Induction Heating: In industrial processes like metal forging, melting, and annealing, IGBTs are the core of high-frequency power supplies. They enable rapid, precise, and clean heating by generating a powerful alternating magnetic field, offering far greater efficiency and control than traditional heating methods.
Conclusion: IGBTs – More Than a Component, an Enabling Technology
A review of these application fields reveals a common thread: a relentless demand for high power, high efficiency, and precise control. This is precisely where the IGBT module delivers its core value.
However, an IGBT is not merely an electronic component; it is an Enabling Technology.
- It is what makes regenerative braking in an EV a reality.
- It is what makes the efficient DC-to-AC conversion of solar power possible.
- It is what makes the precision energy-saving control of industrial motors achievable.
These critical system-level functions are directly enabled by the superior performance of IGBTs. This technology is not just an engine driving global megatrends like electrification, automation, and decarbonization—it has elevated its own value from a single device to one of strategic importance, solidifying its role as a decisive force in the modern industrial and energy revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What exactly does an IGBT do in an electric car?
A: In an EV, the IGBT is the core of the motor controller. It performs two main functions: first, it converts DC power from the battery into AC power to drive the motor, controlling the vehicle’s speed and acceleration. Second, it enables regenerative braking, capturing kinetic energy during deceleration and storing it back in the battery to extend the driving range.
Q2: Why do solar inverters and wind turbines need IGBTs?
A: Solar panels produce DC power, and wind turbines produce variable-frequency AC power. Neither can be directly used by standard appliances or fed into the grid. IGBTs, inside inverters and converters, efficiently and reliably transform this raw power into the stable, grid-compliant AC power that our society runs on.
Q3: What is the core advantage of an IGBT module?
A: The IGBT module’s main advantage is its hybrid design, combining the best features of two different transistors. It has the high input impedance and voltage-driven control of a MOSFET (making it easy to control) and the low conduction losses and high current capacity of a Bipolar Junction Transistor (making it highly efficient and powerful). This unique combination makes it the ideal switch for high-power, high-voltage applications requiring precise and efficient control.
