Content last revised on January 7, 2026
Semikron SKD 25/16 Three-Phase Diode Bridge Rectifier | 1600V 25A Technical Analysis
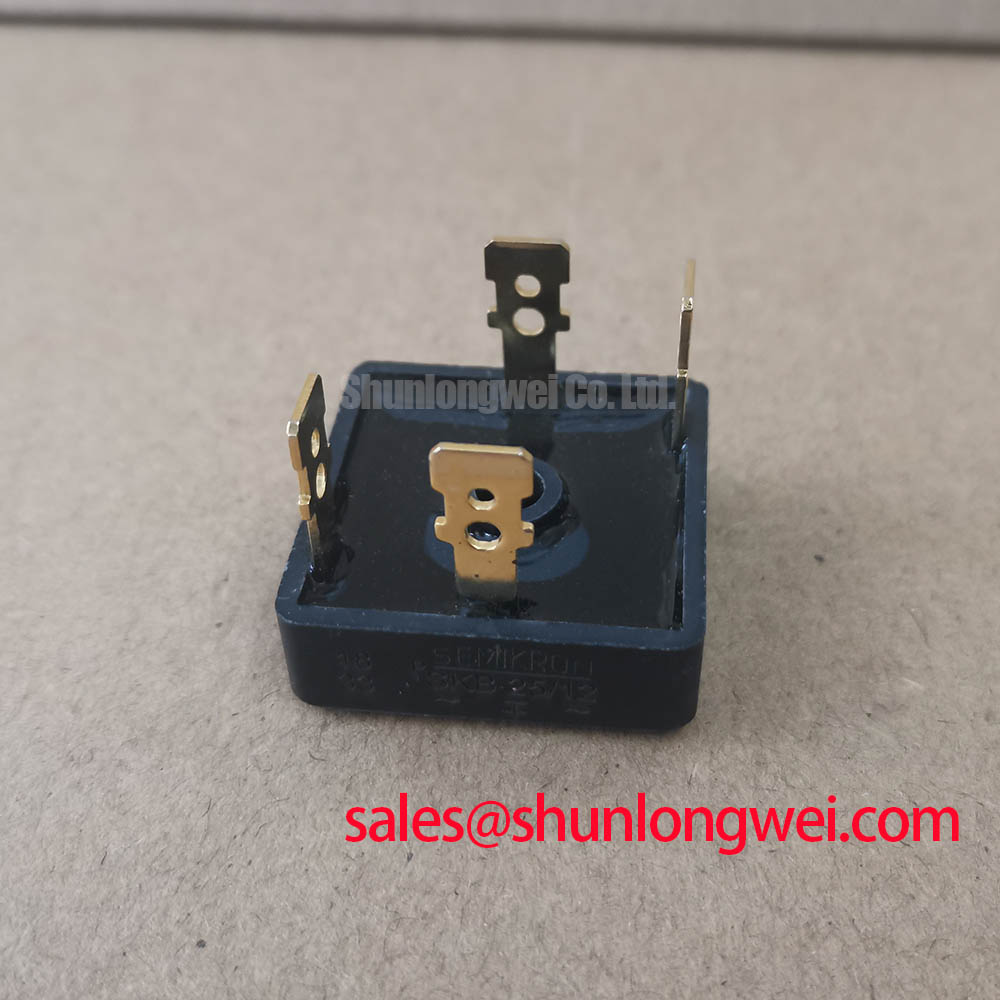
The Semikron SKD 25/16 is a high-performance three-phase diode bridge rectifier designed for robust power conversion in industrial environments requiring 1600V blocking capabilities and a 25A forward current rating. Engineered within the compact SEMIPONT 1 package, this module provides engineers with a reliable solution for input rectification in variable frequency drives (VFDs) and power supplies where thermal efficiency and high surge current handling are non-negotiable.
For systems prioritizing high-voltage isolation and thermal stability in 480V industrial line applications, this 1600V module is the optimal choice.
Top Specs: 1600V V_RRM | 25A I_D (T_c=100°C) | SEMIPONT 1 Package.
Key Benefits: High voltage overhead for transient protection; direct mounting on heat sinks for simplified assembly.
What is the primary benefit of its 1600V rating in 480V systems? It provides a critical safety margin against mains voltage spikes and transients, significantly reducing component-level failures.
Application Scenarios & Value
Achieving System-Level Benefits in Industrial Power Conversion
In industrial motor control, specifically for Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), the input stage must handle significant inrush current and potential line voltage fluctuations. The SKD 25/16 serves as a robust front-end rectifier. Consider an engineering scenario involving a 15kW motor drive operating on a standard 480V three-phase grid. During start-up, the DC bus capacitors draw a massive initial current. The SKD 25/16, with its high surge current rating (I_FSM), ensures the module survives these repetitive stress events without degrading the silicon junctions.
For engineers designing systems with higher power demands, such as 75kW or above, moving toward higher current modules like the SKD100/16 offers a Vces/V_RRM of 1600V but with significantly higher current handling. Conversely, for low-voltage signal processing or auxiliary power stages, the SKD 25/02 provides a 200V alternative. Integrating the SKD 25/16 into UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supplies) or Battery Charging Systems ensures long-term reliability by leveraging its high T_j_max of 150°C. This thermal headroom is critical when the module is deployed in confined enclosures or high-ambient environments typical of heavy machinery.
The selection of this module aligns with the growing demand for high-efficiency power systems, where the low forward voltage drop (V_F) translates directly into reduced power losses and lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
Key Parameter Overview
Decoding the Specs for Enhanced Thermal Reliability
The following table summarizes the critical technical parameters for the SKD 25/16, sourced from the official Semikron technical documentation.
| Parameter | Value | Engineering Significance |
|---|---|---|
| V_RRM (Reverse Blocking Voltage) | 1600 V | Provides protection against peak transient voltages in 400V-600V networks. |
| I_D (Forward Current @ T_c=100°C) | 25 A | Defines the continuous DC output capability under typical operating conditions. |
| I_FSM (Surge Forward Current @ 10ms) | 370 A | Crucial for handling inrush current during capacitor charging at power-up. |
| V_F (Forward Voltage @ 75A) | 1.60 V (typ) | Determines the conduction losses; lower values enhance system efficiency. |
| R_th(j-c) (Thermal Resistance) | 1.5 K/W | Indicates efficiency of heat transfer from junction to the module base. |
Download the SKD 25/16 datasheet for detailed specifications and performance curves.
Technical & Design Deep Dive
A Closer Look at the Pressure-Contact and SEMIPONT Chassis
A defining characteristic of the SKD 25/16 is its SEMIPONT 1 packaging. In power electronics, think of the V_RRM rating as the height of a levee: a 1600V rating means the "levee" is significantly higher than the standard "tides" of a 480V AC line, ensuring that even unexpected surges do not overflow and cause catastrophic shorts. The module utilizes a screw-terminal design for power connections and a metal base plate for heat dissipation, facilitating easy integration into chassis-mounted systems.
The internal diode topology is optimized for Low Forward Voltage Drop. By reducing V_F, the SKD 25/16 minimizes the heat generated per ampere of current. This is akin to a one-way turnstile in a stadium: if the turnstile is hard to push (high V_F), the crowds (current) expend more energy and generate more heat just getting through. Because the SKD 25/16 turnstile is highly efficient, it can handle a steady stream of 25A without requiring oversized cooling solutions, thereby increasing the power density of the overall VFD or Inverter system.
Industry Insights & Strategic Advantage
Addressing Reliability Standards in the Era of Grid Stability
As industrial grids face increased instability due to the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, the robustness of the input rectification stage has become a strategic priority. The SKD 25/16 addresses this by providing 1600V isolation, which is increasingly required for compliance with global standards such as IEC 61800-3 for adjustable speed electrical power drive systems.
In the context of Industry 4.0, where machinery is expected to operate with minimal downtime, the use of high-voltage rectifiers reduces the risk of field failures due to line disturbances. The SKD 25/16 is particularly valuable in DC-link applications for robotic servo drives, where precise power delivery must be maintained even in harsh electromagnetic environments. By selecting components with established thermal cycling capabilities and high V_RRM overhead, procurement teams mitigate the long-term risk of maintenance-heavy life cycles.
FAQ
Engineering Queries Regarding the SKD 25/16 Module
- How does the 1600V V_RRM rating affect MTBF in a 480V application?
By providing a blocking voltage that is roughly 3.3 times the RMS line voltage, the SKD 25/16 significantly reduces the probability of dielectric breakdown during transient overvoltages, directly extending the Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) compared to 1200V alternatives. - Can the SKD 25/16 be used in parallel for higher current applications?
While possible, diode paralleling requires careful attention to thermal symmetry and forward voltage matching. For higher current needs, it is generally more reliable to transition to a single module like the SKD100/16 to avoid current hogging issues. - What is the significance of the 370A I_FSM rating for DC bus charging?
The 370A surge rating allows the module to withstand the short-duration peak current that occurs when a DC-link capacitor is initially connected to the AC line, often eliminating the need for complex pre-charge circuitry in smaller systems. - How does the SEMIPONT 1 package impact thermal design?
The package features an isolated metal base plate, allowing multiple SKD 25/16 modules to be mounted on a single common heatsink, which simplifies mechanical assembly and optimizes the thermal management of the power cabinet. - Is the SKD 25/16 compatible with high-frequency switching environments?
As a standard recovery rectifier, it is optimized for 50/60Hz mains rectification. While it can handle the DC link of high-frequency systems, it is not intended for high-frequency PWM switching; for those applications, fast-recovery or Schottky diodes would be required.
From an engineering perspective, the SKD 25/16 represents a mature, well-documented solution for standard bridge rectification. Its reliability is rooted in the balance between its high 1600V blocking voltage and its efficient thermal dissipation via the SEMIPONT 1 interface. For designers, this module minimizes the complexity of surge protection and heat sink sizing, providing a predictable performance profile for demanding industrial electronics.